In recent years, gambling and its potential impact on mental health has garnered significant attention. With the rise of online casinos, sports betting platforms, and other forms of gambling readily available, it’s essential to address the question: Is gambling a mental illness? While gambling is not classified as a mental disorder in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5), excessive gambling can lead to various mental health issues and addictive behaviors. This article will explore the relationship between gambling and mental health, shedding light on the potential risks and consequences associated with excessive gambling.
Understanding Gambling Addiction
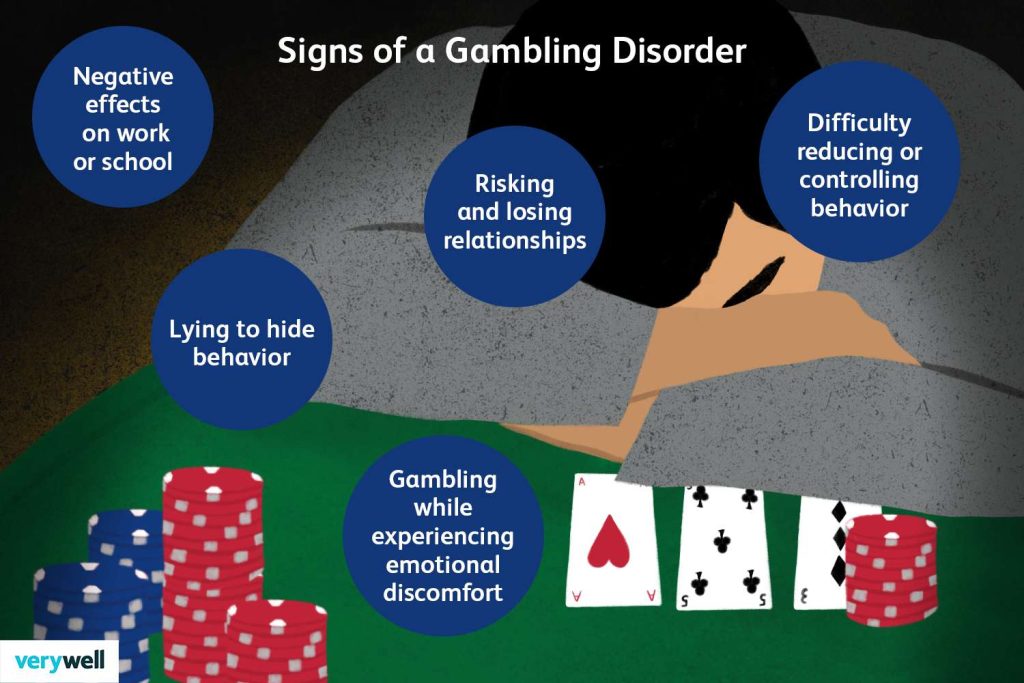
Although not officially recognized as a mental illness, gambling addiction, also known as gambling disorder, shares many similarities with substance use disorders. It is characterized by a compulsive urge to gamble, an inability to control or stop gambling, and continued gambling despite adverse consequences. Individuals with gambling addiction often experience an intense thrill or high while gambling, leading to a vicious cycle of chasing losses and seeking that euphoric state again.
The Link Between Gambling and Mental Health
Research consistently shows a correlation between problem gambling and various mental health conditions. Many individuals who engage in excessive gambling may already have pre-existing mental health issues, such as depression, anxiety disorders, or substance abuse problems. However, it’s important to note that excessive gambling can also contribute to developing or worsening mental health disorders.
Depression and Gambling
Depression and gambling often go hand in hand. The constant cycle of winning and losing and the unpredictability of gambling outcomes can exacerbate depressive symptoms and make it challenging to break free from the addiction. The stress and financial strain caused by gambling losses can lead to feelings of hopelessness, despair, and even suicidal thoughts.
Anxiety Disorders and Gambling
Anxiety disorders, including generalized and social anxiety, can be triggered or intensified by excessive gambling. The fear of financial ruin, the pressure to win, and the stress associated with taking risks can significantly impact a person’s mental well-being. Moreover, individuals with anxiety disorders may turn to gambling as a means of escape or temporary relief, further perpetuating the cycle of addiction.
Substance Abuse and Gambling
The relationship between gambling and substance abuse is complex and interconnected. Both gambling and substance use activate similar reward pathways in the brain, leading to a co-occurring addiction. Many individuals with gambling addiction also struggle with drug or alcohol abuse. The presence of a dual diagnosis requires comprehensive treatment to address both the gambling addiction and the substance abuse issue simultaneously.
Seeking Help and Treatment Options
Recognizing the potential impact of excessive gambling on mental health is crucial. If you or someone you know is struggling with gambling addiction, seeking professional help is essential. Various treatment options are available, including therapy, support groups, and specialized gambling addiction programs. Mental health professionals can provide the necessary guidance and support to help individuals overcome their addiction and regain control of their lives.
Preventing Gambling-Related Mental Health Issues
Prevention plays a vital role in mitigating the negative consequences of gambling on mental health. Here are some strategies to consider:
- Awareness and Education: Increasing public awareness about the potential risks of excessive gambling and educating individuals about responsible gambling practices can help prevent gambling-related mental health issues.
- Financial Management: Establishing and sticking to a strict budget for gambling activities can minimize financial strain and reduce the likelihood of experiencing significant losses.
- Support Networks: Building a solid support system of friends, family, or support groups can provide emotional support and encouragement during recovery.
- Healthy Coping Mechanisms: Encouraging the adoption of healthy coping mechanisms, such as exercise, mindfulness

